
Cognitive rehabilitation is a form of rehabilitation that focuses on improving cognitive abilities in individuals who have experienced cognitive impairments due to various factors such as brain injury, stroke, or neurodegenerative diseases. Unlike other forms of rehabilitation that may target physical or motor skills, cognitive rehabilitation specifically targets cognitive functions such as memory, attention, problem-solving, and language skills. Injury Rehabilitation The goal of cognitive rehabilitation is to help individuals regain or improve their cognitive abilities, ultimately enhancing their overall functioning and quality of life.
There are several common cognitive impairments that can benefit from cognitive rehabilitation. These include but are not limited to, traumatic brain injury, stroke, dementia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and learning disabilities. Cognitive impairments can manifest in various ways, such as difficulties with memory, attention, executive functioning, language, and visuospatial skills. Cognitive rehabilitation aims to address these specific impairments through targeted interventions and strategies.
Gait AnalysisCognitive rehabilitation helps individuals regain or improve their cognitive abilities through a variety of techniques and strategies. These may include memory training exercises, attention and concentration exercises, problem-solving tasks, language therapy, and compensatory strategies. The specific approach used in cognitive rehabilitation will depend on the individual's unique needs and goals. By engaging in these targeted interventions, individuals can strengthen their cognitive skills, improve their ability to perform daily tasks, and enhance their overall cognitive functioning.
Exercise Therapy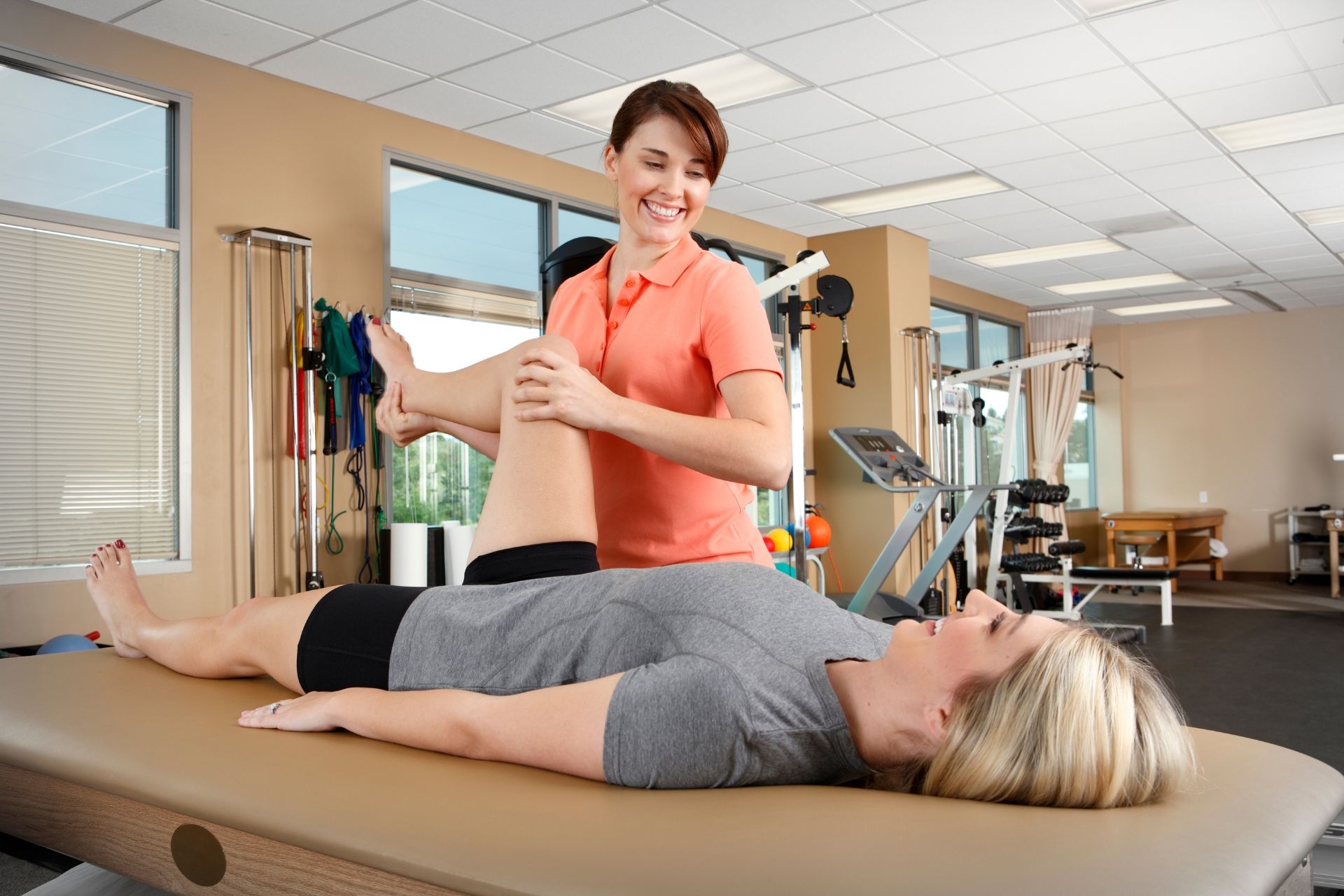
In cognitive rehabilitation, there are specific techniques and strategies that are commonly used to address cognitive impairments. These may include cognitive training exercises, which involve repetitive practice of specific cognitive tasks to improve performance. Additionally, compensatory strategies may be employed, such as using memory aids or implementing organizational systems to help individuals cope with cognitive difficulties. The use of technology, such as computer-based programs or mobile applications, can also be incorporated to enhance the effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation interventions.
Cognitive rehabilitation can be effective for individuals with degenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, although the extent of improvement may vary depending on the stage and severity of the disease. While cognitive decline associated with degenerative conditions is often progressive and irreversible, cognitive rehabilitation can still play a valuable role in managing symptoms, slowing down the progression of cognitive decline, and improving quality of life. It can help individuals maintain their cognitive abilities for longer periods, adapt to changes, and maximize their functional independence.
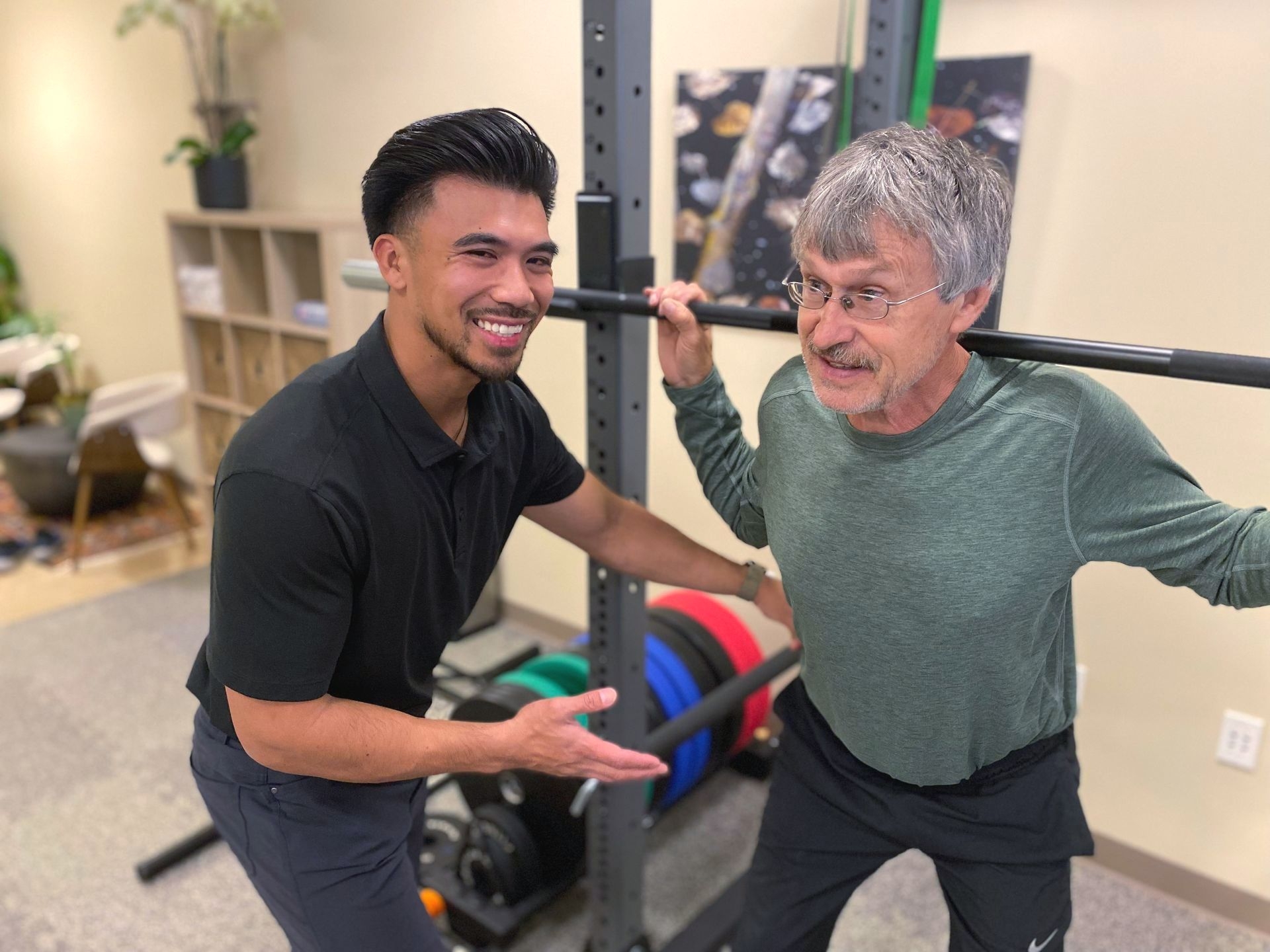

When it comes to potential risks or side effects associated with cognitive rehabilitation, they are generally minimal. However, it is important for individuals undergoing cognitive rehabilitation to work with qualified professionals who can tailor the interventions to their specific needs and monitor their progress. In some cases, individuals may experience frustration or fatigue during cognitive rehabilitation sessions, but these are typically temporary and can be managed with appropriate support and pacing. Musculoskeletal Health It is crucial for individuals to communicate any concerns or difficulties they may have during the rehabilitation process to ensure their needs are addressed effectively.
The duration of cognitive rehabilitation can vary depending on the individual's specific needs and goals. Some individuals may require a few weeks or months of intensive rehabilitation, while others may benefit from ongoing maintenance sessions over a longer period. The expected outcome of cognitive rehabilitation is to improve cognitive functioning, enhance daily functioning, and improve overall quality of life. While the extent of improvement may vary, individuals can expect to see positive changes in their cognitive abilities, increased independence in daily activities, and improved overall well-being as a result of cognitive rehabilitation.
Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation
Physical therapy can be a valuable component in the management of lymphedema. Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, typically in the arms or legs, due to impaired lymphatic drainage. Physical therapy interventions, such as manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, exercise, and education, can help reduce swelling, improve lymphatic flow, and enhance overall function and quality of life for individuals with lymphedema. By utilizing specialized techniques and modalities, physical therapists can assist in reducing edema, promoting tissue healing, and preventing complications associated with lymphedema. Additionally, physical therapists can provide guidance on self-care strategies, including skin care, exercise, and compression garment use, to help individuals manage their condition effectively. Overall, physical therapy plays a crucial role in the comprehensive management of lymphedema, providing individuals with the tools and support they need to optimize their health and well-being.
Paraneoplastic pemphigus is a rare autoimmune blistering disorder that is associated with an underlying malignancy. While physical therapy does not directly treat paraneoplastic pemphigus, it can play a supportive role in the rehabilitation process. Rehabilitation techniques for paraneoplastic pemphigus may focus on improving range of motion, strength, and functional mobility. Physical therapists may utilize exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities such as heat or cold therapy to help manage pain and inflammation. Additionally, they may provide education on proper body mechanics and postural awareness to prevent further complications. The goal of physical therapy in paraneoplastic pemphigus is to optimize the patient's physical function and quality of life while working in collaboration with the patient's medical team.
Physical therapy can play a crucial role in the management of Huntington's disease. By focusing on improving mobility, strength, balance, and coordination, physical therapy can help individuals with Huntington's disease maintain their independence and quality of life. Specific exercises and techniques, such as gait training, range of motion exercises, and balance training, can address the motor symptoms associated with the disease. Additionally, physical therapy can also provide education and support to both the individual with Huntington's disease and their caregivers, helping them understand the disease progression and providing strategies to manage symptoms effectively. Overall, physical therapy can be an integral part of a comprehensive treatment plan for individuals with Huntington's disease, promoting functional abilities and enhancing overall well-being.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management and treatment of ankle impingement. By employing a variety of techniques and exercises, physical therapists aim to reduce pain, improve range of motion, and restore function to the affected ankle joint. They may utilize manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilizations and soft tissue mobilizations to address any restrictions or tightness in the ankle joint and surrounding structures. Additionally, they may prescribe specific exercises to strengthen the muscles around the ankle, improve stability, and correct any imbalances or weaknesses that may be contributing to the impingement. These exercises may include ankle range of motion exercises, proprioceptive training, balance exercises, and strengthening exercises for the calf, foot, and ankle muscles. Physical therapists may also incorporate modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation to help reduce pain and inflammation in the ankle. Overall, physical therapy provides a comprehensive and individualized approach to managing ankle impingement, helping individuals regain optimal function and return to their daily activities.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of spinal stenosis. By employing a variety of techniques and exercises, physical therapists can help alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall function in individuals with this condition. One of the primary goals of physical therapy is to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine, which can help provide better support and stability to the affected area. Therapists may also use manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilization and soft tissue massage, to reduce pain and improve joint mobility. Additionally, they may incorporate stretching exercises to increase flexibility and improve range of motion. By tailoring treatment plans to the specific needs of each patient, physical therapy can effectively manage spinal stenosis and improve quality of life.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing osteoarthritis by providing targeted interventions to improve joint function, reduce pain, and enhance overall quality of life. Through a combination of manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and modalities such as heat or cold therapy, physical therapists aim to alleviate pain, increase range of motion, and strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected joints. They also educate patients on proper body mechanics and joint protection techniques to minimize further damage. Additionally, physical therapists may recommend assistive devices, such as braces or orthotics, to provide support and stability. By tailoring treatment plans to individual needs, physical therapy helps individuals with osteoarthritis regain mobility, improve functional abilities, and manage their condition effectively.
Physical therapy is an effective treatment option for individuals with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS). POTS is a condition characterized by an abnormal increase in heart rate upon standing, often accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and fatigue. Physical therapists utilize a variety of techniques to address the underlying causes of POTS and improve symptoms. These may include exercises to improve cardiovascular fitness, such as aerobic conditioning and interval training. Additionally, physical therapists may employ techniques to improve postural control and balance, such as balance training and proprioceptive exercises. They may also utilize manual therapy techniques to address any musculoskeletal imbalances or restrictions that may be contributing to symptoms. Overall, physical therapy aims to improve cardiovascular function, enhance postural stability, and alleviate symptoms associated with POTS, ultimately improving the individual's quality of life.
Physical therapy can play a crucial role in the rehabilitation of individuals with aortic dissection. Aortic dissection is a serious condition that involves a tear in the inner layer of the aorta, the main artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. The goal of physical therapy in aortic dissection rehabilitation is to improve overall cardiovascular fitness, enhance mobility, and promote functional independence. Physical therapists may utilize a variety of techniques, including therapeutic exercises, cardiovascular conditioning, and manual therapy, to address specific impairments and limitations caused by the condition. Additionally, they may provide education on lifestyle modifications, such as proper body mechanics and activity pacing, to prevent further complications and promote long-term health. By working closely with a physical therapist, individuals with aortic dissection can optimize their recovery and regain their quality of life.